1.1 Basic Biology Review
Amino Acids & Proteins
AA structure
AA Types
Steps of Protein synthesis
Cellular Respiration (Aerobic)

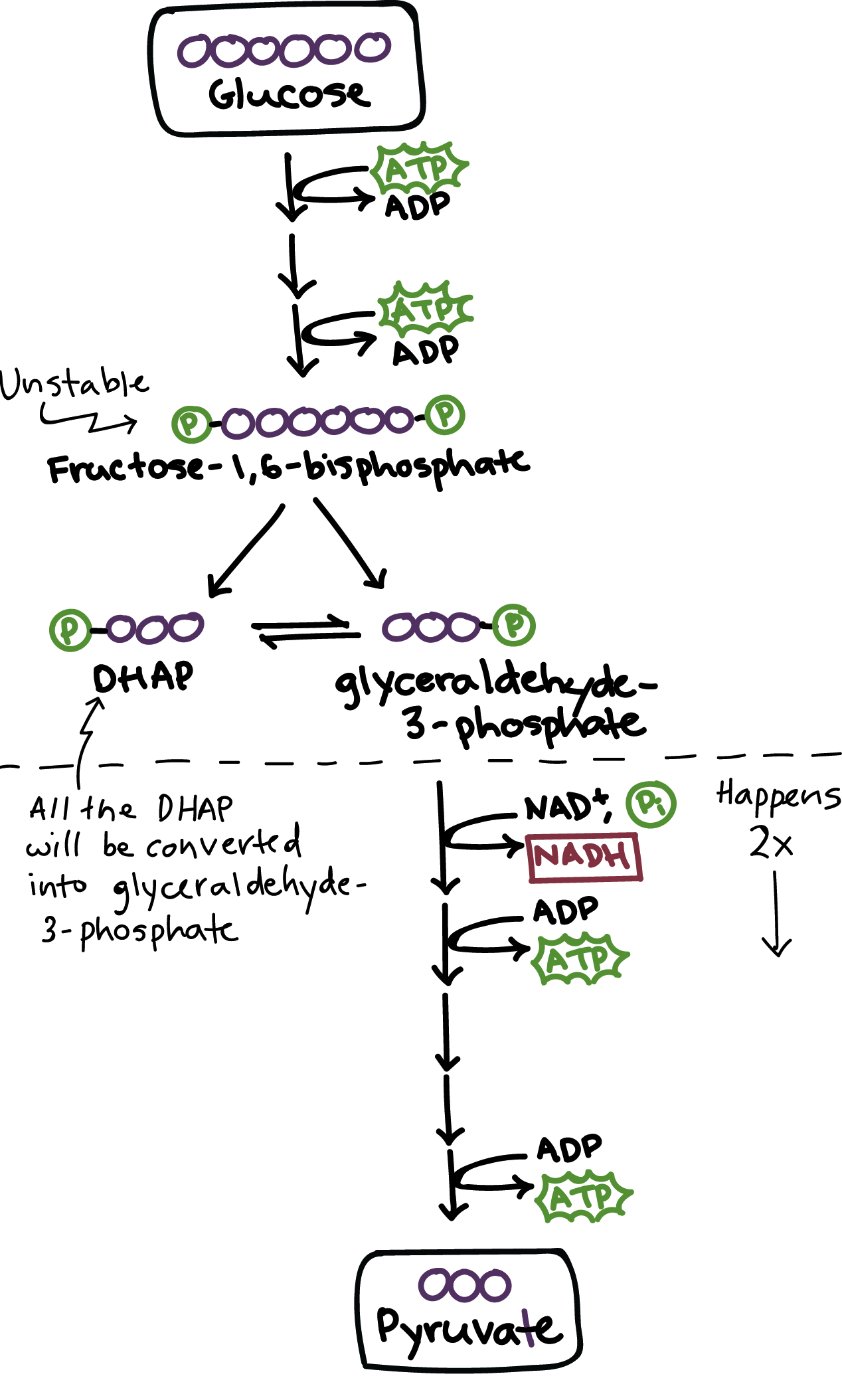
Glycolysis
Krebs Cycle / Citric acid

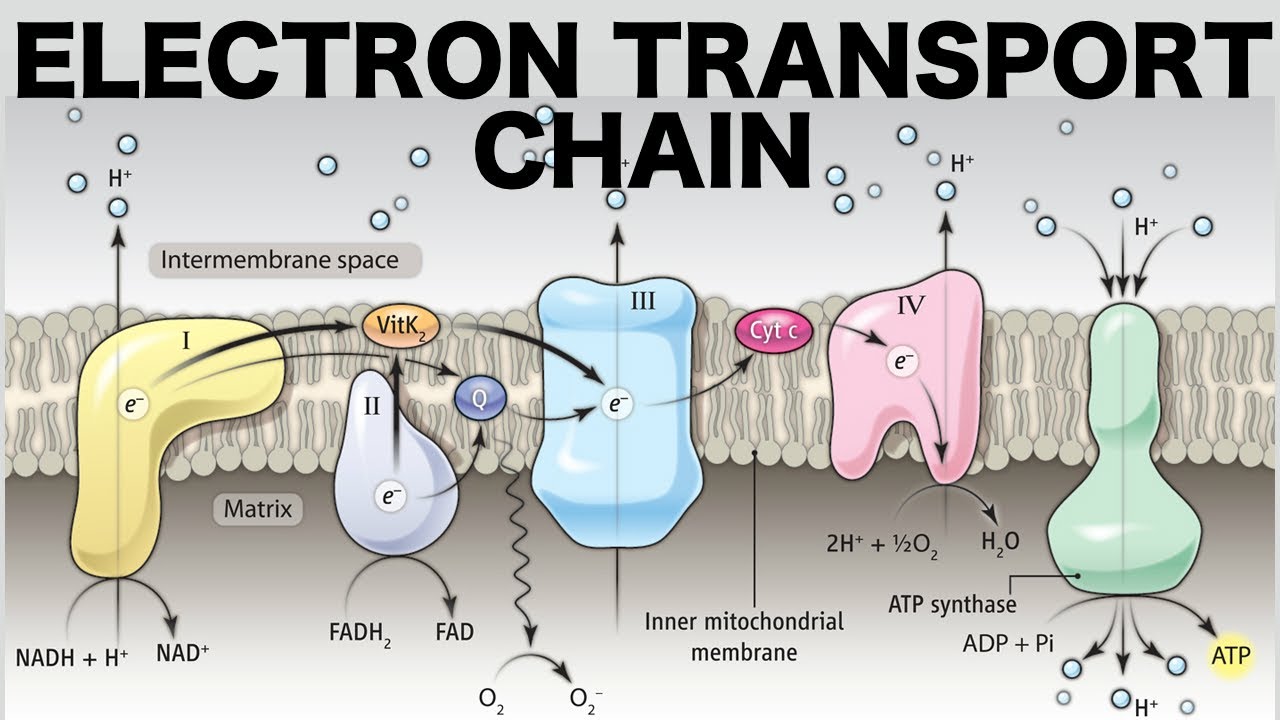
Electron Transport Chain
Other
Last updated